

Large amounts of these substances or the presence of certain other materials may be abnormal.ĮU = Ehrlich units. Of note, serum osmolality increased to 329mOsm/kgwhile serum ADH, urine specific gravity and urine osmolality remained unchanged. †Normal findings detected by microscopic examination can include a few RBCs (especially in menstruating women), WBCs, epithelial cells, bacteria, yeast cells, crystals (eg, Ca oxalate, triple phosphate, amorphous phosphates and urates), sperm, and unidentifiable materials. Laboratory Test: The patient was then subjected to a 2-hour water deprivation test followed by another blood chemistry profile and urinalysis. In pathological urines, direct measurement of urine osmolality should be used.Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigen (AENA)Īnti–cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodiesĪntidiuretic hormone (ADH arginine vasopressin)Īnti–double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies, IgGĪntineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (cANCA)Īnti–smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA) titer Pathological urines had significantly poorer correlation between USG and osmolality than "clean" urines. For an increase in SG of 0.010, predicted osmolality increases by 182 mosm/kg/H(2) O for the reagent strip and 203 mosm/kg/H(2)O for refractometry. At a pH of 7 and with an USG of 1.010 predicted osmolality is approximately 300 mosm/kg/H(2)O for either method. The variables affecting the correlation included pH, ketones, bilirubin, urobilinogen, glucose, and protein for the reagent strip and ketones, bilirubin, and hemoglobin for the refractometry method. This study demonstrated that USG obtained by both reagent strip and refractometry had a correlation of approximately 0.75 with urine osmolality.
The relationships were analyzed by linear regression. The other variables considered were pH, protein, glucose, ketones, nitrates, bilirubin, urobilinogen, hemoglobin, and leukocyte esterase. Urinalysis data on these subjects were used to determine the correlation between USG and osmolality, adjusting for other variables that may impact the relationship. Out of these, 253 USG's were measured by automated refractometry and 251 USG's were measured by reagent strip. Using our laboratory's records, we retrospectively gathered data on 504 urine specimens on patients on whom a simultaneously drawn USG and an osmolality were available. We studied the correlation of USG obtained by either method with a concurrently obtained osmolality. USG is measured either by refractometry or by reagent strip. Specific gravity will be high and fractional excretion of sodium will also increase. 1.035 and a higher osmolality than the blood plasma. 1.015 and a higher osmolality than the blood plasma. Specific gravity, in the context of clinical pathology, is a urinalysis parameter commonly used in the evaluation of kidney function and can aid in the. 1.010 and the same osmolality as the blood plasma. 1.005 and a lower osmolality than the blood plasma.

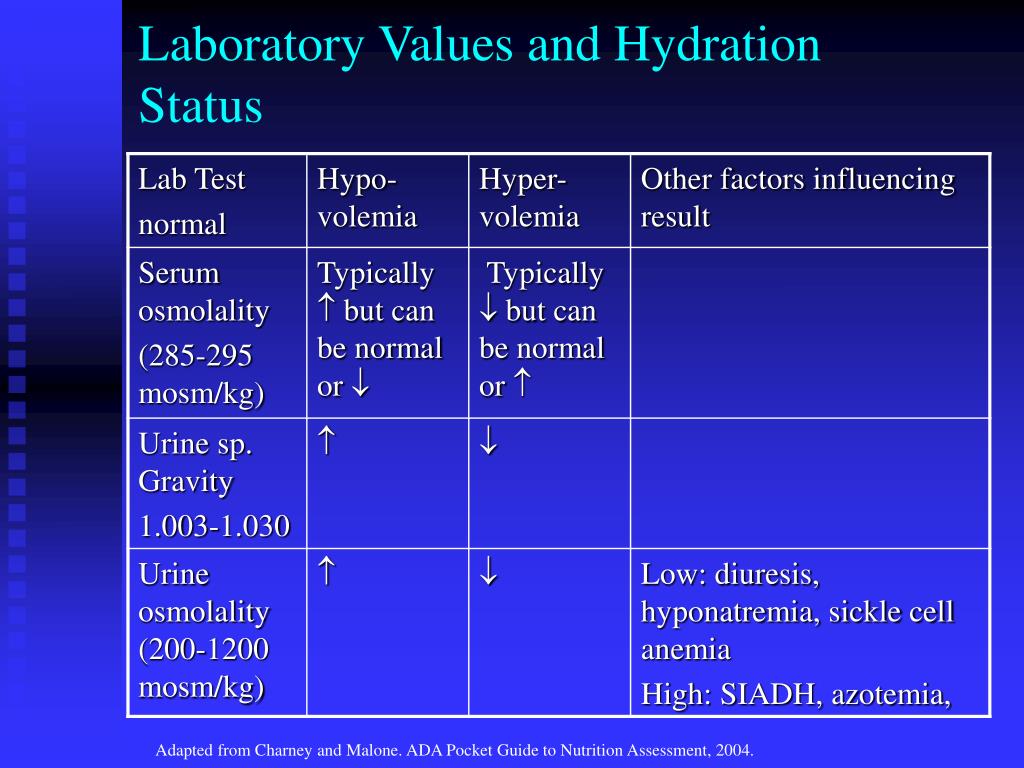
Urine volume will decrease unless the cause of dehydration is polyuria or diuretic use. The ultrafiltrate in the urinary space of the glomerulus has a specific gravity of A. Data were reanalyzed to generate reference values for urine indices (i.e., urine osmolality, urine specific gravity (USG), and urine volume) and urine color. Serum osmolality will exceed 300 mOsm/kg and serum sodium will exceed 150 mEq/L. Urine specific gravity (USG) is often used by clinicians to estimate urine osmolality. Drinking urine or seawater for survival Laboratory values in hypertonic dehydration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
